Johari’s Window
- Aria Fox
- April 8, 2023
The Johari Window is a psychological model that was designed for use in self-help groups to help members become more intimate with their peers, while at the same time learning to become more honest with themselves. The concept helps people understand the extent of their self-awareness compared to how others perceive them. It was developed in the mid-1950s by two psychologists who combined their first names to label the idea: Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham (Jo-Hari).
How much of ourselves do we hide from others? How open are we to letting people see us as we are? In fact, how prepared are we to admitting our own flaws and strengths?
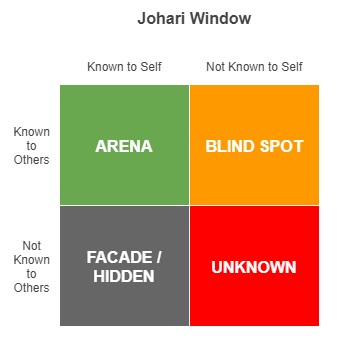
The Arena quadrant consists of adjectives, both positive and negative, that the subject uses to describe him or herself, as well as those that peers identify in him or her. The Façade or Hidden quadrant consists of things that subjects are aware of about themselves but that they conceal from others.
The Blind Spot quadrant is the reverse—that is, it describes qualities that subjects are unaware of, but that peers perceive about them.
Finally, the Unknown quadrant describes qualities unknown to either the subject or others.
One therapeutic target for subjects may be the expansion of the Arena quadrant at the expense of both the Unknown and Blind spot quadrants. By increasing self-knowledge and disclosing more of one’s own qualities to others, ordinarily protected by the Facade quadrant, one increases the opportunities for friendship and intimacy.
A disproportionately large Blind spot can be a source of misunderstanding and friction. Subjects who know little about themselves—less than others do— may be regarded as self-centered, difficult, or inauthentic. When neither the subject nor his or her peers are aware of the subject’s deeper qualities, as in the Unknown quadrant, the result may be dangerous. A person this isolated can harm others without those around them suspecting that the potential existed. Violent individuals can fall into this category—preying on unsuspecting victims. Johari’s Window is a useful tool in group work and self-help endeavors.
